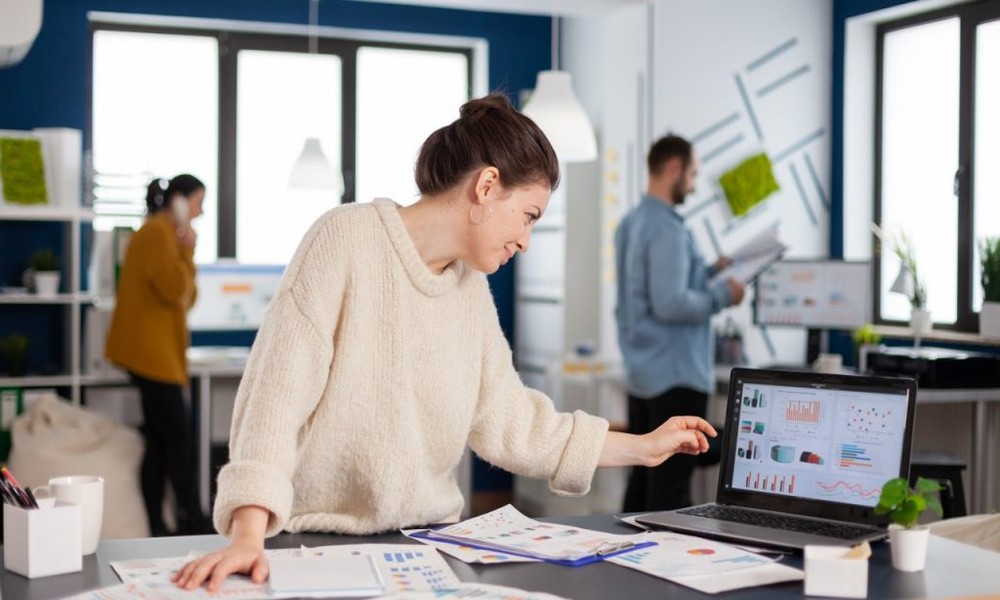
Data is more powerful than ever. Companies rely on it to make smarter decisions, improve services, and grow faster. If you want to enter this growing field, earning a Degree in Business Data Analysis can give you a strong start. This degree equips you with the skills to understand and use data effectively, helping businesses solve problems and make better decisions. But to succeed in business analytics, you need a combination of technical skills, soft skills, and a clear understanding of your role in the business.
Business analytics is not just about handling data-it’s about turning that data into insights that can guide real business decisions. Let’s dive deeper into what a business analytics professional does and the skills you need to thrive.
Understanding the Role of Business Analytics Professionals
Business Analyst vs. Business Analytics Professional
Many people confuse business analysts with business analytics professionals. While their roles sound similar, they focus on different aspects of a business.
- Business Analyst: Their primary role is improving business processes and operations. They study how a business works, identify areas for improvement, and help implement solutions. Business analysts often coordinate between clients and development teams to ensure products or services meet business needs. For example, a business analyst might work with a client to redesign a customer service process and ensure that the new system is efficient and meets expectations.
- Business Analytics Professional: Their focus is on data. They collect, analyze, and interpret data to provide actionable insights. These insights might improve marketing campaigns, enhance products, or improve customer experience. Unlike business analysts, they rely on numbers, trends, and statistical models to guide decisions.
Think of it this way: business analysts improve how a business works, while business analytics professionals use data to show what actions will lead to success.
Key Soft Skills for Business Analytics Professionals
Technical skills are essential, but soft skills make a business analytics professional truly effective. Here are the most important:
- Clear Communication: Presenting data findings in a simple, understandable way is critical. A good analyst can tell a story with data through clear writing, presentations, and visuals. For instance, instead of showing raw numbers, they might create charts that clearly demonstrate trends in customer behavior.
- Curiosity and Inquisitiveness: Business analytics professionals should have a natural curiosity to explore data, ask questions, and connect pieces of information. This curiosity helps uncover hidden patterns that can lead to better decisions.
- Problem-Solving Ability: Analysts use logic, statistics, and predictive models to solve business problems. If sales are declining in one region, they might analyze customer data to find the cause and suggest ways to improve performance.
- Critical Thinking: Analysts must carefully choose which data is useful and which is not. They should question assumptions, consider multiple perspectives, and focus on information that will genuinely guide decision-making.
- Data Visualization Skills: Presenting data visually helps stakeholders quickly understand insights. Whether it’s graphs, dashboards, or infographics, visual representation makes complex information easy to digest.
- Detail-Oriented While Thinking Big: Analysts must manage detailed data while also understanding the broader impact of their recommendations. Every insight should tie back to business goals, like increasing profits or improving customer satisfaction.
Technical Skills and Tools for Business Analytics
Essential Technical Skills
Business analytics professionals need a mix of technical skills to handle the growing volume of data in modern businesses.
- SQL: SQL is the language used to interact with databases. Analysts use it to extract, filter, and analyze data efficiently. For example, if a company wants to know which products sold best last month, SQL queries can quickly provide this information.
- Programming Languages: R and Python are commonly used for statistical analysis and data modeling. Python is particularly popular because it can handle both data analysis and automation tasks. While you don’t always need to know programming, having some knowledge makes it easier to work with large datasets.
- Statistical Software: Tools like Excel, SPSS, SAS, Sage, and Mathematica allow analysts to organize and analyze data without programming. These tools are useful for generating reports, running simulations, or creating forecasts.
- Data Visualization Tools: Programs like Tableau, Power BI, and Google Data Studio help turn complex data into easy-to-read visual dashboards. Businesses use these dashboards to track performance in real time.
The Four Types of Analytics
Business analytics skills are applied differently depending on the type of analytics.
1. Descriptive Analytics – What is happening now?
Descriptive analytics focuses on understanding current business performance. By collecting and summarizing data, analysts can identify trends, such as which products are selling well or which marketing campaigns are most effective. Real-time dashboards help companies monitor operations and quickly react to changes.
2. Diagnostic Analytics – Why is it happening?
Diagnostic analytics digs into past data to uncover reasons behind business outcomes. For example, if website traffic dropped last month, diagnostic analytics can identify the cause-perhaps a campaign ended or a competitor launched a promotion.
3. Predictive Analytics – What is likely to happen?
Predictive analytics uses statistical models and forecasting to predict future events. This can help businesses anticipate customer behavior, forecast sales, or prepare for market changes. For instance, an e-commerce company might use predictive models to stock the right products for an upcoming season.
4. Prescriptive Analytics – What should we do next?
Prescriptive analytics goes one step further by recommending actions based on data insights. If predictive analytics shows a likely drop in sales, prescriptive analytics could suggest targeted promotions, pricing adjustments, or new marketing strategies to counteract it.
How to Build a Career in Business Analytics
A career in business analytics can be highly rewarding. Here are some practical steps:
1. Education: Start with a Degree in Business Data Analysis or a related field. This provides foundational knowledge in statistics, programming, and data visualization.
2. Develop Technical Skills: Learn SQL, Excel, Python or R, and at least one visualization tool like Tableau or Power BI
3. Build a Portfolio: Work on projects that show your ability to analyze real-world data. This could be class projects, internships, or personal projects. Employers value candidates who can demonstrate practical skills.
4. Enhance Soft Skills: Communication, critical thinking, and problem-solving are equally important. Practice explaining complex data in simple terms.
5. Stay Updated: The field of business analytics is always evolving. Keep learning about new tools, techniques, and industry trends to stay competitive.
Why Business Analytics Professionals Are in High Demand
As businesses realize the impact of data on strategy and operations, the demand for skilled business analytics professionals continues to grow. Companies need people who can turn raw data into meaningful insights, predict trends, and make recommendations that drive success. By combining technical skills with strong soft skills, business analytics professionals become invaluable assets to any organization.
With the right education, practical experience, and dedication, a career in business analytics can be both exciting and highly rewarding. A Degree in Business Data Analysis is a strong first step toward becoming a skilled professional in this thriving field.